Difference Between Flocculated And Deflocculated Suspension
To clearly understand the difference between flocculated and deflocculated suspensions, you need to start from the grassroots of knowing what flocculation and reformulation are.
The main distinction between flocculation and deflocculation is that the former involves the clumping of small particles to produce globules, although the latter entails the distribution of globules to create a stable colloid.
When a substance is in a suspension, its particles are mixed with a liquid but are not dissolved. Suspensions are categorized by focusing on the electrokinetic properties of the solid trapped particles in the suspension: flocculated suspensions and deflocculated suspensions.
With the knowledge of the electrokinetic properties, you can then categorize the suspension into flocculated suspension and deflocculated suspension.
In chemistry, flocculation is the process whereby the colloidal particles in a suspension become aggregated. These aggregates can settle to the bottom of the liquid and become sediment. Based on the electrokinetic nature of the dispersed phase, suspensions can be classified as flocculated suspension or deflocculated suspension.
The primary distinction between flocculated and deflocculated suspensions is that settlement in a flocculated suspension is instantaneous, whereas settlement in a deflocculated suspension is slow. Suspensions are classified as flocculated or deflocculated based on the electrokinetic nature of the dispersed particles.
What exactly is a Flocculated suspension?
A flocculated suspension is one in which the suspension’s droplets have flocculated. Flocculation is the process of obtaining aggregated colloidal particles from a suspension of colloids. As a result, a flocculated suspension is made up of multiple aggregates, and so this type of suspension will sediment quickly.
Sedimentation is the process by which aggregates or suspended particles settle at the bottom of a liquid. Particle aggregation results in large aggregates that can function as large individual particles. When these aggregates settle, a large number of particles settle with them.
The sedimentation frequency, therefore, is very fast. These aggregates are referred to as floccules. Because of gravity, floccules can sediment more quickly than tiny ones.
Because floccules have a loose structure with pores that can absorb and retain liquid, the sediment that forms in a flocculated suspension is larger than anticipated. As a result, the final sediment volume is greater than anticipated.
A Deflocculated Suspension: Definition
A suspension that has not undergone flocculation is said to be deflocculated. As a result, there are no aggregates like floccules. In this case, a single colloid particle functions as a particle. These solitary particles settle during sedimentation.
Dispersed particles emerge as discrete entities in a deflocculated suspension. Since smaller particles rather than large floccules are settling, the rate of sedimentation is slow. The slow sedimentation prevents the liquid from becoming entrapped in the sediment.
The final sediment has a smaller volume than a flocculated suspension. Even after the sediment has formed, the supernatant of this suspension will still be cloudy.
Difference Between Flocculated and Deflocculated Suspension
Because the aggregated suspension is often unsightly, partial aggregation is often a desired goal because it resists caking and adds aesthetic qualities to a suspension formulation. To maintain dosage accuracy, a pharmaceutical suspension should be dispersible with only gentle shaking.
Flocculated suspensions, show rapid sedimentation, resulting in loose sediment, whereas deflocculated suspensions show slow, but compact, sedimentation. A deflocculated system has the advantage of slow sedimentation, which allows for uniform dosing.
The primary distinction between a flocculated and a deflocculated suspension is the speed at which sedimentation occurs in the former as against the latter which occurs at a slower rate.
Definitions
Flocculation is a chemical and physical or pharmaceutical phenomenon that develops as a result of a weakening of the electrical forces that normally repel the dispersed suspension particles.
A loosely aggregated structure known as a floc result when particles with less repelling force approach one another under these circumstances.
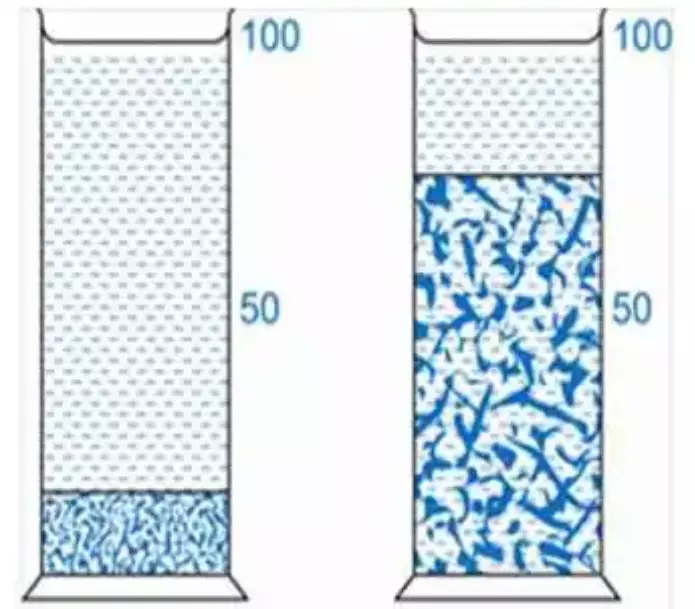
The individual particles in a deflocculated suspension stay as discrete, separated units and settle gradually. The slow rate of particle settling keeps the individual particles of this suspension from entrapping any liquid medium and causes them to become compact, which results in the formation of cake.
Volume or Size Of The Sediment
A flocculated suspension has a significant amount of sediment in it. While Deflocculated Suspension: Deflocculated suspensions have less sediment in them overall.
Sediment’s Porosity
Flocculated Suspension: Flocculated suspensions produce porous sediments. While Deflocculated suspensions result in the formation of non-porous sediments.
Suspension Re-dispersion
Flocculated Suspension: By agitating a flocculated suspension, sediment that has formed can be easily re-dispersed. While Deflocculated Suspension: By agitation, the re-dispersion of sediment created in a deflocculated suspension is challenging.
To guarantee consistent dosage, a pharmaceutical suspension ought to be re-dispersible with only mild agitation. A deflocculated system has the advantage of having a slow sedimentation rate, which allows for uniform dosing.
Therefore, depending on the desired end product of the suspension, you can then determine if it will be a flocculated suspension or deflocculated suspension.
Tabular Representation Of The Differences Between Flocculated And Deflocculated Suspension
| Defloculated Suspension | Flocculated Suspension |
| A suspension that has not flocculated is said to be deflocculated. | A flocculated suspension has had its particles flocculated. |
| Hard cakes are usually formed because of tightly packed sediments. | There is no formation of a hard cake because the sediments formed are usually loosely packed. |
| There is the presence of a low volume of sediment. | There is the presence of a high volume of sediments. |
| Absence of floccule | Presence of floccules |
| The sediment re-dispersion cannot be easily achieved with agitation | Simply agitation can easily lead to the re-dispersion of sediments. |
| It leads to the formation of none porous sediments | There is a formation of porous sediments. |
| Elegant appearance because of the uniform appearance of the deflocculated suspension. | Particles of the dispersed phase easily separate from the dispersion medium and this makes flocculated suspensions lack elegance. |
| The particles of the dispersed phase in a deflocculated suspension remain as separate entities. | There is an aggregation of the particles of the dispersed phase and invariably, the formation of a loose networklike structure. |
Read Also: How to Start Pharmacy Business in Nigeria
Conclusion
The main distinction between flocculation and deflocculation is that the former involves the clumping of small particles to produce globules, a suspension can therefore be classified as being flocculated or deflocculated.
The primary distinction between flocculated and deflocculated suspensions is that settlement in a flocculated suspension is instantaneous, whereas settlement in a deflocculated suspension is slow.

![Contact Addresses Of All Pharmacies In Lagos State ([year]) Contact Addresses Of All Pharmacies In Lagos State](https://eucarlpharmacy.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/ezgif.com-gif-maker-72-1.webp)
![Pharmacist Salary Structure In Nigeria [year]: See What They Earn Pharmacist Salary Structure In Nigeria](https://eucarlpharmacy.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Pharmacist-Salary-Structure-In-Nigeria.jpg)
![NeoLife Products Price List in Nigeria ([year]) NeoLife Products Price List in Nigeria](https://eucarlpharmacy.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/NeoLife-Products-Price-List-in-Nigeria-768x768.webp)


![Current Prices of Vitamin E Oil & Capsule in Nigeria ([year]) Current Prices of Vitamin E Oil & Capsule in Nigeria](https://eucarlpharmacy.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Prices-of-Vitamin-E-768x512.jpg)