What Is Leptomeningeal DIsease? Symptoms and Treatment
The leptomeningeal disease is a type of cancer that affects those membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord, CSF (cerebrospinal fluid), and the leptomeninges. The leptomeningeal disease has no known cure. Instead, healthcare professionals concentrate on treatment to stop the spread of cancer, lessen symptoms, and preserve the quality of life.
The leptomeningeal disease has no known cure; instead, healthcare professionals concentrate on treatment to stop cancer from spreading, lessen symptoms, and preserve the quality of life. Despite the rarity of the leptomeningeal disease, doctors are finding more cases as cancer patients live longer.
The leptomeningeal disease is a dangerous, currently incurable consequence of late-stage or advanced cancer. Most patients who receive treatment for this illness survive three to six months after their diagnosis. Without treatment, patients survive for about a month following diagnosis. However, each person’s tumor and circumstances are particular.
Disease Of The Leptomeninges (Leptomeningeal Disease)
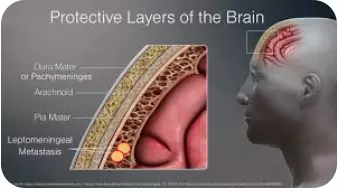
Cancer of the leptomeninges, the membranes that cover your brain and spinal cord, and the cerebrospinal fluid is referred to as leptomeningeal disease (also known as leptomeningeal metastases).
It takes place when leptomeninges and CSF are affected by advanced cancer that has spread from one section of the body.
A multifocal metastasis to the leptomeninges, which is made up of the pia mater, arachnoid, and subarachnoid space, results in the leptomeningeal disease, a late-stage consequence of systemic malignancies.
Symptoms Of Leptomeningeal Disease
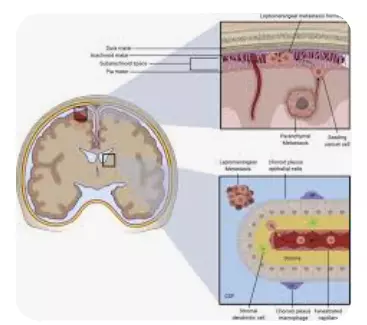
Cerebrospinal fluid is continuously produced by the body in the ventricles of the brain. It is a blood-based substance that moves from the brain’s center to the back, down the spinal cord, and then back up. The fluid then travels over the top of the brain before returning to the bloodstream. CSF is replaced by the body numerous times every day.
Neurological issues can arise if tumor cells infiltrate the CSF and persist to spread all across the central nervous system. Although there are several leptomeningeal disease symptoms, these are the most prevalent:
- Vomiting and nauseous.
- Headache.
- Gait modifications or difficulties walking.
- Confusion and adjustments in behavior, attitude, or alertness.
- Leg and back aches.
- Loss of hearing.
- Weakness or numbness in the buttocks or legs.
- Issues with urinating, losing control of urination, or pooping.
- Seizures.
- Vision difficulties, such as double vision.
Depending on where the cancer cells settle, the leptomeningeal illness can result in nearly any neurological issue.
Read Also: Hole in The Heart: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Causes Of Leptomeningeal Disease
The leptomeningeal disease develops when a cancerous tumor grows and invades the leptomeninges and cerebrospinal fluid in your body. This is a substantial occurrence and signifies an advanced and aggressive phase of malignancy.
The inner portion of the meninges is called the leptomeninges. The brain creates a transparent fluid called CSF that surrounds the entire central nervous system and comes into contact with your leptomeninges. But if something prevents it, this fluid normally drains through a network of veins.
Numerous neurologic symptoms can result from cancer that has metastasized to the leptomeninges and CSF. It can also disrupt the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid and put pressure on the brain.
Diagnosis And Tests For Leptomeningeal Disease
In addition to performing a spinal tap (lumbar puncture) to retrieve cerebrospinal fluid, which they can then analyze for the presence of cancer cells, medical professionals use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and/or spine to detect leptomeningeal disease.
It can occasionally be tricky to diagnose leptomeningeal disease since MRI cannot always figure out the abnormality or even because an MRI can look perfect if the malignancy progression is only microscopic.
Management And Treatment Of Leptomeningeal Disease
Sadly, medical professionals are unable to treat this illness. Instead, they concentrate on approaches to lessening symptoms and halting the progression of cancer.
Treatments change depending on the type of cancer that affected your cerebrospinal fluid and leptomeninges, its location, and your general health. The leptomeningeal disease is most frequently treated with radiation and chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy
Medical professionals may utilize anticancer medications, depending on the type of cancer and available treatments.
These can be administered orally, intravenously, or directly into your cerebrospinal fluid via ventricular access. But because medications have a very difficult time entering the central nervous system, chemotherapy is given intrathecally.
i. Intra-thecal chemotherapy
In non-nodular and non-bulky Leptomeningeal disease, intrathecal administration is the most popular way to give chemotherapeutic drugs, albeit its effectiveness in comparison to systemic administration and choice of regimen are poorly understood.
For the treatment of Leptomeningeal disease, intrathecal injections of methotrexate, cytarabine, and thiotepa are frequently used.
ii. Systemic chemotherapy
Systemic therapies for leptomeningeal disease are thought to improve patient survival, according to multiple reports.
Some authors don’t include intrathecal medicines at all in patients with responsive tumors because they believe this is the more important part of treatment.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy might aid with neurological function and symptom relief. For patients with symptomatic leptomeningeal disease, radiation treatment is a crucial method of palliative care.
Cranio-spinal radiation is normally avoided because marrow toxicity makes it difficult for the patient to tolerate subsequent chemotherapy regimens.
While those with symptomatic spinal lesions are candidates for focused radiation, those with cerebral involvement often receive entire brain radiotherapy.
Surgical Procedures
These include the insertion of intraventricular catheters and ventriculoperitoneal shunting. When bulky Leptomeningeal disease causes obstructive hydrocephalus, shunting is used.
Diet
Leptomeningeal metastases have not been successfully treated with a specific diet, but nutritional support is always beneficial for cancer patients.
Prevalence Of Cancers And Leptomeningeal Disease
The leptomeningeal disease manifests in about five percent of the overall cancer patients. The following types of cancer are the most prevalent in those who have the condition:
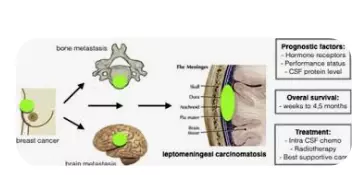
Breast Cancer
The most frequent cancer associated with leptomeningeal disease is breast cancer. In between 3 and 5 percent of breast cancer patients, the leptomeningeal disease will manifest.
According to studies, women with triple-negative breast cancer or lobular breast cancer, a subtype of the illness, are more likely to get the leptomeningeal disease than women with other forms of breast cancer.
Melanoma
Leptomeningeal disease will manifest in about 5 percent of total melanoma patients.
Lung cancer
Leptomeninges and CSF can be affected by leptomeningeal and small-cell lung cancers, respectively. Between 4 percent and 7 percent of persons with non-small cell lung cancer, according to medical professionals, will develop leptomeningeal metastases. The leptomeningeal disease affects about 11 percent of persons with small-cell lung cancer.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Leptomeningeal disease affects 5%–10% of those with non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Between 1 and 10 percent of those with acute lymphocytic leukemia develop leptomeningeal illness.
Preventing Leptomeningeal Disease
Leptomeningeal disease risk cannot be decreased, which is a sad fact. Other than avoiding or treating primary cancer, there are presently no proven prophylactic strategies for halting the spread to the leptomeninges. Leptomeningeal metastases should ideally be treated as soon as possible.
Read Also: What Is Hypomenorrhea? Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Conclusion
The leptomeningeal disease is a dangerous, currently incurable consequence of late-stage or advanced cancer.
There is some palliative management like the use of chemotherapy, radiation, surgical procedures, and eating diets good in cancer cases but nothing can be done to prevent the progression of an already developed leptomeningeal disease.
Some cancer cases also predispose one to leptomeningeal disease.